

In late September, the White House accelerated a two-track strategy on trade: impose immediate, headline-grabbing duties while opening fresh national-security investigations that could justify wider tariffs later.
Late on September 25 (ET), President Trump said the U.S. will levy steep tariffs on imported branded/patented pharmaceuticals beginning October 1, 2025, with carve-outs for countries covered by trade agreements or where manufacturers are actively building U.S. plants. Hospital groups warned of potential risks to patient access if supplies are disrupted. Subsequent clarifications and allied briefings suggest the effective rate for partners bound by existing agreements will be capped near 15%, aligning with trade-deal commitments, even as 100% duties were initially touted for non-covered sources.
In parallel, the Commerce Department (BIS) formally launched Section 232 national-security investigations into imports of PPE, medical devices/equipment, and separately robotics and industrial machinery. These probes, initiated September 2 and publicly noticed September 24–26, start a 270-day clock that could end in recommendations for tariffs or quotas across a wide list of items: from syringes, infusion pumps, and surgical gloves to industrial robots, CNC tools, and ovens. Pharmaceuticals are already the subject of a separate 232 review, so the new medical-equipment probe does not cover prescription drugs.
The ripple effects of these tariff shifts are already sparking debate across industries. For pharmaceuticals, a new tariff wall on branded drugs gives Washington fresh leverage in trade talks, but it also threatens to drive up costs and create short-term shortages where domestic alternatives don’t yet exist. Negotiations in recent weeks have already scaled back some of the harsher proposals, with key partners likely to see caps closer to 15% under existing agreements.
Hospitals and patient advocates warn that even brief disruptions in drug availability could carry serious risks, especially for therapies with no easy substitutes. Their concern is less about the theory of trade policy and more about the day-to-day reality of keeping treatments flowing without interruption.
Beyond medicine, the scope of the Section 232 investigations stretches into hospital consumables and the industrial robotics that underpin U.S. manufacturing. If national-security risks are found, tariffs could extend into these areas, raising costs for hospitals and factories alike. At the same time, policymakers see this as a way to push supply chains back onto U.S. soil. The catch: America still relies heavily on suppliers in Japan, Germany, China, and South Korea for advanced robotics and machinery, dependencies that won’t be easy to unwind.
Oct 1, 2025: Pharma duties begin, with exemptions/limits for trade-deal partners and for firms actively building U.S. manufacturing. Expect agency guidance to define qualifying “build-in-America” investments and certify exclusions.
Through Q2 2026: Commerce/BIS runs the 232 investigations (up to 270 days) and sends recommendations to the President; tariffs or quotas could follow sector-by-sector.
Exemptions & compliance mechanics for pharmaceuticals, how companies document U.S. build-outs or trade-agreement coverage
Scope lists in the 232 probes (HS lines for PPE, devices, robotics, machinery)
Allied responses, EU and Germany are already signaling that, under agreements, pharma rates for partners should not exceed 15%
Knock-on sectors (trucks, furniture, cabinets were flagged alongside pharma in recent briefings).
For historical context on tariff classifications, see the USITC HTS archive, which maintains a record of past HS/HTS code changes.
Big and bulky fulfillment doesn’t have to block global growth. Learn how ecommerce brands can ship oversized products internationally with real-time freight rates, duty-paid delivery, and zero foreign inventory.
Ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China continue to be the defining story of the 2019 global economy. What started off as an ongoing dialogue about the economic relationship between the two largest economies in the world has transformed

President Trump issues Executive Order to stop overlapping tariffs on imports under national security and trade actions, ensuring duty rates remain targeted and non-cumulative. Effective retroactively from March 4, 2025.

In the hospitality and hotel sectors, the success of a project often hinges on countless elements working together seamlessly. Among these, shipping Furniture, Fixtures, and Equipment (FF&E) plays an integral role, often influencing a project's timeline,

Based on the latest insights from the 2025 National Trade Estimate Report, here’s a practical breakdown of the most pressing trade challenges across the United States’ top 10 goods trading partners.
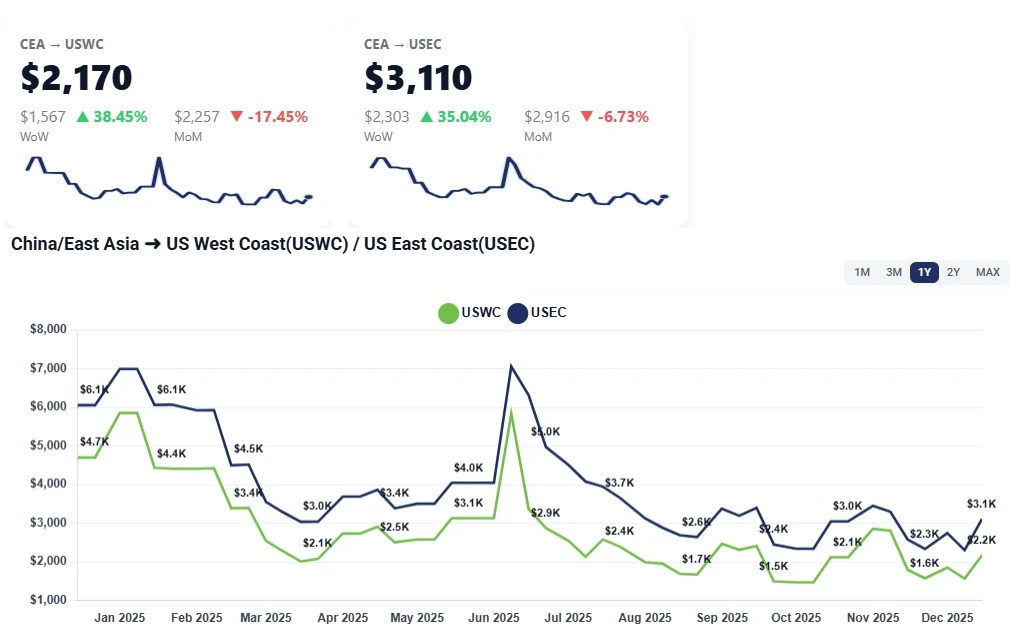
China–US ocean freight rates rose WoW: USWC near $2.1K/FEU and USEC near $2.9–$3.0K as carriers end fixed extensions and hold firm into January.

The International Longshoremen's Association began their strike October 1, 2024, affecting ports running along the east coast and Gulf regions of the United States. See what ports are affected and what this strike can mean for shippers.
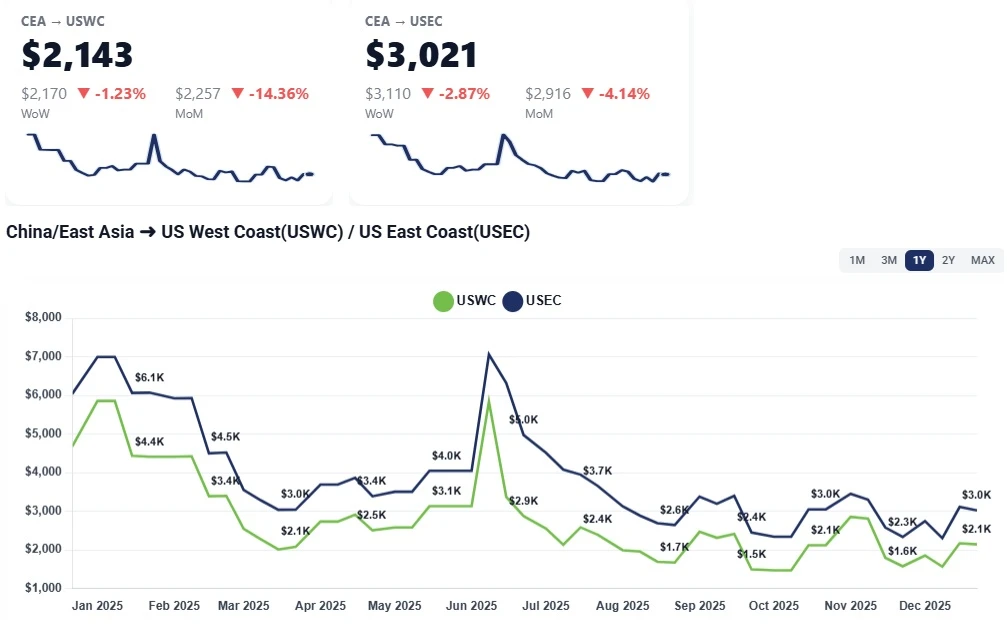
China–US ocean freight rates to the West and East Coasts held steady this week amid a holiday slowdown. Learn what’s driving the flat market and why January GRIs could push prices higher.

Trump’s latest trade deal with China and South Korea cuts tariffs, boosts U.S. exports, and deepens security and economic cooperation.

Learn the top 2 reasons for eCommerce cart abandonment—high shipping costs and slow delivery—and discover actionable strategies to reduce lost sales and boost conversions.